Income Tax Return

As a tax specialist we at RSG Accountants use up to date information about business taxation, tax laws. Our knowledge of client’s particular circumstances assists us to provide them with specific advice and plans for tax minimisation. In addition, with the best accountants available, we organise the preparation and lodgement of income tax returns, for individuals and all types of business entities, and provide the following services in Cragieburn and nearby suburbs.
Tax Return Services Craigieburn
- Tax Returns for Individual taxpayers
- Tax Returns for Sole Traders/ Proprietors
- Tax Returns for companies
- Tax Returns for Partnerships, Trusts including Super funds
How much Tax will be Paid?
Income tax is money paid to the government from the money you earn. It is usually paid throughout the year as you earn the income. For example, if you work for an employer, your employer will deduct tax from each pay and send it to the Australian Taxation Office (ATO) on your behalf.
Marginal Tax Rates 2017 - 2018
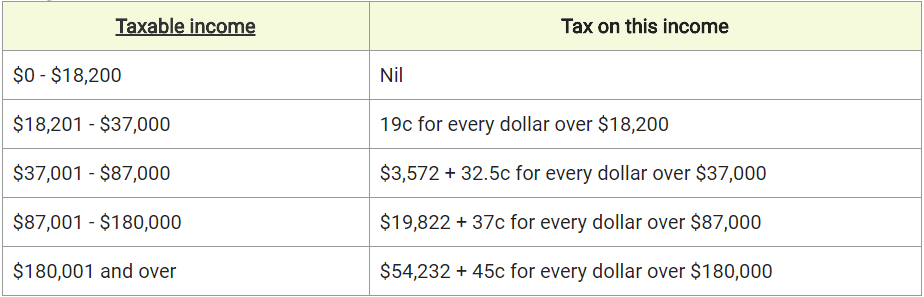
Medicare levy and the surcharge
In addition to income tax, most people will also have to pay a Medicare levy. The Medicare levy is calculated as 2% of your taxable income. It is used to help fund our public health system. Generally, it allows you to visit a doctor or receive treatment at a public hospital free of charge.
Low income earners may have their Medicare levy reduced or may not have to pay it at all. People not entitled to use our Medicare system, such as foreign residents, will not have to pay the Medicare levy either.
High income earning individuals or families who do not have an appropriate level of private patient hospital cover may have to pay a Medicare levy surcharge. This is an extra 1%, 1.25% or 1.5% of their taxable income depending on their income level.
The Medicare levy is charged as part of your yearly income tax assessment. The ATO website has more information on the Medicare levy.
What income is taxable?
Your taxable income is your assessable income minus your tax deductions.
Income that is taxable
Income that you must pay tax on includes money from:
- employment
- pensions and annuities
- most government payments
- investments
- capital gains
- income from trusts, partnerships or businesses
- foreign income.
The ATO has more information on income you must declare in your tax return.
Income that is not taxable
You will not have to pay tax on:
- lottery winnings and other prizes
- small gifts or birthday presents
- some government payments
- child support
- the tax-free portion of your redundancy payment
- government super co-contributions.
The ATO has more details on amounts not included as income.
Reducing your tax payable
You may be able to reduce the amount of tax you pay if you are entitled to any tax deductions or tax offsets (rebates) or if you decide to salary sacrifice.
Tax Deduction
Tax deductions are certain expenses you incurred in order to earn your income. Deductions reduce your taxable income before the tax is calculated.
Common deductions include:
- Work-related expenses
- Self-education expenses
- Charitable donations
- The cost of managing your tax affairs (like paying an accountant).
You can find out more about deductions on the ATO’s income and deductions webpage.
Tax Offset
Tax offsets directly reduce the amount of tax owing, and are applied after the tax has been calculated.
Common tax offsets include offsets for:
- low income earners
- taxpayers with a dependent relative
- pensioners and senior Australians
- the taxable portion of a superannuation income stream.
You can find out more about tax offsets on the ATO’s offsets and rebates webpage.
Salary Sacrificing
Salary sacrificing is another way you can reduce your tax bill. Salary sacrificing, also known as salary packaging, is when you put some of your pre-tax income towards a particular benefit before you are taxed. Common salary sacrifice benefits include superannuation and motor vehicles.
How to avoid getting a tax bill
If you’ve earned income where no (or not enough) tax has been withheld, you can take steps to reduce the likelihood of receiving a tax bill. For example you could:
- voluntarily make PAYG instalments – If you earn income as a sole trader or from investments, you can choose to make voluntary PAYG instalments.
- prepay tax – You can make tax prepayments any time to make it easier to manage your tax. Prepaid amounts are held by the ATO towards your expected bill, unless you or your agent request a refund.
- increase employer tax withheld – You can ask your employer to increase the amount of tax withheld from your pay. This is known as an upward variation.
- consider the impact of a capital gain – If you sell a capital asset for more than what you paid for it you will have made a capital gain. Consider the impact the amount and timing of the gain will have on your assessable income.